Close
Jack Sharples and Andrew Judge
(Bibliographical details at end)
Amidst the current tensions about Russian military deployment in Crimea, there has been considerable speculation in the European and American media about the security of Russian gas supplies to the EU. Such speculation is generated by a combination of concerns over the level of dependency on Russian gas imports faced by several EU member states and fears that the Russian government considers gas exports to be an ‘energy weapon’ that can be deployed against its former Soviet neighbours. Given that almost 60 percent of Russian gas exports to the EU (not including Finland and the Baltic States) are delivered via Ukraine, any suspension of Russian gas supplies to Ukraine would have a significant effect on European imports of Russian gas.
Much of the commentary on this issue that emphasises the Russian ‘energy weapon’ fails to examine the economic aspect of Russian-Ukrainian gas relations. Furthermore, much of the contemporary discussion of EU energy security and dependence on Russian gas supplies fails to address the inherently regional nature of this dependency. The states of Central and South-Eastern Europe are far more dependent on Russian gas supplies in general, and gas transit via Ukraine in particular, than their western European counterparts.
In the context of current tensions, this short article will address both of these shortcomings by analysing the likelihood of a suspension of Russian gas supplies to Ukraine and the impact of such a suspension on EU gas imports. Firstly, we highlight the importance of Naftogaz’s commercial debts to Gazprom and the politically negotiable nature of gas prices in contracts between Gazprom and Naftogaz as a source of instability in the Russia-Ukraine gas relationship. Secondly, we draw on a variety of statistical sources to illustrate and explain the impact of a potential suspension in gas transit via Ukraine on different EU member states. In pursuing both of these aims, we look to draw lessons from previous supply disruptions, particularly that of January 2009.
Russia-Ukrainian gas relations: recurring debt and politically negotiable gas prices
Despite the prominence of political relations between Russia and Ukraine in considerations of the security of Ukrainian gas transit, we believe that the current situation can be best understood as a continuation of the long-running commercial dispute between Naftogaz in Ukraine and Gazprom in Russia over gas debts and pricing. The fact that both Gazprom and Naftogaz are state-owned companies, and that Russian and Ukrainian government officials participate in their bilateral gas negotiations, combined with the strategic importance of the bilateral gas relationship to both parties, means that Russia-Ukraine gas relations have an undeniable political component. However, it is our opinion that the commercial relationship between Gazprom and Naftogaz, and especially the issues of gas prices and payment discipline, remain at the heart of the Russia-Ukraine gas relationship.
Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia continued to supply gas to its post-Soviet neighbours at substantially lower prices than it charged importers in Western Europe. Despite these discounts, Ukraine consistently struggled to pay for gas supplies and at various points during the 1990s, supplies to Ukraine were cut off to enforce payment discipline. Because these disputes did not result in major disruptions to European supplies, they passed relatively unnoticed in Western Europe. At this time, prices for Russia’s gas exports to both Eastern and Western Europe were index-linked to international oil prices, with the pricing differentials generated by differences in coefficients in the pricing formulae. Following the upsurge in international oil prices from 2003, the gap widened between the price of Russian gas exports to Western Europe and the price of Russian gas exports to former Soviet states, such as Ukraine. The commercial imperative for Gazprom to raise prices for Ukraine and other former Soviet states was boosted by Russia’s changing political relations with the states of the region, following the ‘Rose Revolution’ in Georgia (2003) and the ‘Orange Revolution’ in Ukraine (2004/05).
The January 2006 Russia-Ukraine gas dispute was the result of Gazprom’s attempts to impose higher prices on its Ukrainian counterpart, Naftogaz. Negotiations were conducted in the context of the tense political relations between Kyiv and Moscow that had followed the ‘Orange Revolution’ and the election of a pro-Western Ukrainian government. Naftogaz refused to accept these higher prices and Gazprom cut off supplies to Ukraine on the 1st of January 2006 for three days. This led to supply shortfalls in several EU member states, although the main reason for the shortfalls appeared to be that Ukraine was taking gas that was in transit to Europe. Despite the shortfalls, supplies to end users in the EU were not cut off during dispute.
The dispute was resolved by signing an agreement to supply Ukraine with a mixture of full price Russian gas and lower priced gas from Turkmenistan (Stern, 2006). This agreement proved to be only temporary, however, unravelling throughout 2008 as Naftogaz accumulated increasing debts to Gazprom (between $1.6bn and $2.2bn). A year earlier, the Russian government announced plans to increase domestic Russian gas prices to ‘European netback’ (European prices minus customs duty and the cost of transportation) by 2011. In March 2008, Gazprom had also agreed to start paying similar netback prices for its gas imports from Central Asia (including Turkmenistan). This meant that there was a clear economic case for ending the discount to Ukraine. In a scenario that would be repeated in late 2013, negotiations between Gazprom and Naftogaz were centred on Naftogaz’s debts to Gazprom, and the price at which Naftogaz would purchase gas from Gazprom. The fact that the price at which Naftogaz would buy gas from Gazprom was considered politically negotiable, with governmental figures from Ukraine and Russia involved in the negotiations, meant that the price was uncertain, and that relations between Naftogaz and Gazprom were more unstable. Also notable was the failure of the two parties to make use of any dispute resolution mechanisms, such as those provided by the Energy Charter Treaty, to resolve the issue of Naftogaz’s outstanding debts.
As in 2006, negotiations between Ukraine and Russia ended without a definitive resolution. In the absence of a new gas supply contract, Gazprom halted all supplies for Ukrainian consumption on the 1st of January. After European energy companies began reporting a fall in volumes delivered via Ukraine from the 2nd of January, Gazprom accused Naftogaz of siphoning off supplies. Naftogaz responded with the claim that it was entitled to take a certain amount of gas to maintain pressure in the pipeline system (technical gas), and that transit volumes were being delivered in full. On the 6th of January, the supply of Russian gas into Ukraine was reduced significantly, from 214 mcm/d to 60 mcm/d, making full transit impossible. Finally, on the 7th of January, all supplies through Ukraine were shut off, leading to major supply shortfalls in several EU member states. Gazprom blamed Naftogaz for preventing transit supplies from entering Ukraine, while Naftogaz blamed Gazprom for shutting down all gas flows into Ukraine. In the absence of reliable data and monitors, it is impossible to adjudicate. What is clear, is that the suspension of gas transit via Ukraine particularly affected member states in Central and South-Eastern Europe, as well as the non-EU states of Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Macedonia and Moldova, who were heavily dependent on Russian supplies with little or no access to alternative sources (Kovacevic, 2009).
Gas transit via Ukraine was suspended for 13 days. The dispute was resolved when Yulia Timoshenko authorised Naftogaz to sign a new, 10-year supply and transit contract with Gazprom, with European-level prices linked to oil, discounted by 20% for the first year (Pirani, Stern, and Yafimava, 2009). In January 2009, the price of Brent Crude was approximately $43 a barrel. By January 2010, when the discount ran out, Brent Crude had rebounded to $76 a barrel, dragging Ukrainian gas prices upwards with it. The combination of rising prices and the end of the discount led the Ukrainians to protest that they had been locked into an unfair contract. Upon his election as president in March 2010, one of Yanukovych’s first priorities was to secure a new gas price discount from Russia. The result was the ‘Kharkiv Accords’, in which the Ukrainian government would extend Russia’s lease on the Sevastopol naval base (home of Russia’s Black Sea Fleet) from 2017 to 2042. In return, the Russian government would cancel the export duty on gas exported to Ukraine, thus giving Ukraine a 30% discount (limited to $100 per thousand cubic metres).
The four years since the Kharkiv Accords have seen constant bickering between Moscow and Kyiv over gas prices. In February 2011, oil prices returned above $100 a barrel, and have since remained at an annual average of $108-112 per barrel. As a result, Russian gas prices for Ukraine have remained high. Available data suggests a level of approximately $12.50-13.50 per MBtu for the last two years. During that time, spot prices in Europe (NBP, TTF, and ZEE) have remained at a level of $9-11 (East European Gas Analysis). The combination of increased supply-side competition in Europe, high oil prices, lower spot prices, and demands from Gazprom’s largest European clients for contractual renegotiations led to Gazprom offering temporary discounts to its European clients in a bid to retain market share. These developments led Ukrainian politicians to complain that Ukraine was paying far more for its gas than Western European countries. Since 2011, the Ukrainian government has made significant efforts to reduce its gas consumption and imports, as well as seeking alternative gas supplies. Naftogaz imports from Gazprom fell from 45 bcm in 2011 to less than 28 bcm in 2013. Yet Naftogaz continued to accumulate debts to Gazprom. The Russian government has offered Ukraine the ‘Belarusian option’ of gas price discounts in exchange for joining the Eurasian Customs Union or selling Ukraine’s gas transportation system to Gazprom, again illustrating the ‘politically negotiable’ nature of Russia-Ukraine gas relations. Belarus has joined the Customs Union and sold its gas transportation system to Gazprom, but the Ukrainian government has refused to do either.
In December 2013, in the midst of the Kyiv protests, the Russian government announced that Ukraine would receive a 33% discount on its gas prices, from $400 to $268, and that the Russian government would provide its Ukrainian counterpart with a $15bn loan in several tranches. This discount brought Ukrainian gas import prices below those of Russian gas on the German border and even below prices on European spot markets. This move bolstered President Yanukovych, undercut potential alternative European gas supplies to Ukraine, and gave the Ukrainian government the funds to allow state-owned Naftogaz to clear its debts to Gazprom. The first tranche of $3bn was disbursed immediately, but Naftogaz failed to pay its debts to Gazprom. By February, Naftogaz owed $3.25bn for late-2013 and January 2014 deliveries. During the second half of February Naftogaz paid $1.47bn of this debt and asked that the remaining payments be deferred until the 15th of April. On the 17th of February, the Russian Finance Minister, Anton Siluanov, announced that the Russian government was prepared to transfer the second tranche of the loan to Ukraine by buying $2bn of Ukrainian Eurobonds. In light of subsequent events in Kyiv, this second trance was not disbursed.
The potential for a suspension of Russian gas supplies to Ukraine in March-April 2014
In light of the failure of the Ukrainian government to use the Russian loan to clear its gas debts, and Naftogaz’s increasing indebtedness, the Russian government decided to cancel the discount, effective from the 1st of April. On the 4th of March, President Putin told reporters, “If you don’t pay us and your debt is ever-increasing, there is no discount, this makes perfect commercial sense for Gazprom”. This view was echoed by Gazprom spokesman, Sergei Kuprianov, “What is owed is huge, not just for last year, but also debts for current deliveries... agreements on discounts mandated full and timely payment for deliveries”. On the 7th of March, the head of Gazprom, Alexei Miller warned that, “Either Ukraine settles its debt and pays for current deliveries or the risk arises of a return to the situation we saw at the start of 2009”.
This underlines the challenges facing the two parties to this dispute, as well as the Russian and Ukrainian governments. For both Gazprom and the Russian government, the difficulty lies in recovering debts of around $2 billion without pushing Naftogaz into the desperate measures of defaulting on those debts or starting to siphon off volumes destined for Europe. For both Naftogaz and the Ukrainian government, the main difficulty is that they have little prospect of servicing the debt, partly because of the current economic situation in the country and partly because of the massive non-payment for gas supplies by Ukrainian consumers, which deprives Naftogaz of revenue needed to pay for gas imports. The scale of this non-payment by Ukrainian industrial consumers was illustrated in early February, when Naftogaz released a statement claiming that industrial consumers owed Naftogaz $3.1bn, with 37% of this debt ($1.2bn) having been accumulated in the three months from November to January.
The current situation bears comparison to the run-up to previous Russia-Ukraine gas disputes. As in the months prior to the January 2006 dispute, political relations between Russia and Ukraine are currently tense, to say the least. Indeed, relations between Moscow and Kyiv are currently far more strained than they were in December 2008. Naftogaz’s current debts to Gazprom are reminiscent of the 2009 dispute, although if anything, the Ukrainian government appears to be in an even more financially perilous state than it was in January 2009. Finally, political negotiations of the price at which Gazprom sells gas to Naftogaz and plans to cancel the discount also resemble previous negotiations over Ukraine’s proposed accession to the Eurasian Customs Union, Gazprom’s desire for control over Ukraine’s gas transportation system, and the Kharkiv Accords of April 2010.
Whilst we do not believe that the suspension of Russian gas supplies is inevitable, the similarities between the current situation and that prior to previous disputes means that such a suspension of Russian gas supplies to Ukraine, and therefore gas transit via Ukraine, cannot be ruled out. This situation justifies a consideration of the potential impact of the suspension of gas transit via Ukraine on EU imports of Russian gas.
The impact of a Ukrainian transit interruption on EU imports of Russian gas
The role of Russia in EU gas import dependence
The EU’s gas import dependence is the most commonly cited fact used to support claims about EU energy insecurity. This statistic refers to the level of net imports as a share of gross inland consumption. The most recent figure from Eurostat places EU-28 gas dependence at 65.8% of consumption in 2012. With the exception of the Netherlands and the UK, relatively little gas is produced within the borders of the EU, although some member states such as Denmark, Germany, Italy and Romania have a limited amount of domestic production. As a result, approximately two-thirds of EU gas consumption has to be sourced from outside the EU. There are three main suppliers of pipeline gas to the EU – Russia, Norway, and Algeria – along with several other suppliers of liquefied gas, most notably Qatar. Russia was the largest single supplier to the EU in 2012, providing 36.5% of EU gas imports. This gave Russian gas a share of 24.2 percent of total EU gas consumption. For comparison, Norway accounted for 34.2% of EU gas imports in 2012, while Algeria and Qatar provided 14.2% and 9.2%, respectively (Eurogas).
In light of Gazprom’s increased exports to Europe over the past 12 months, a slight fall in Norwegian exports, the re-direction of LNG supplies to the Asia-Pacific market (where prices are higher) and the stability of EU gas consumption, the share of Russian gas in 2013 total EU gas consumption is likely to be slightly higher than in 2012. Indeed, reports suggest that Russia’s share of European gas consumption reached 30 percent in 2013. However, given that Gazprom’s definition of ‘Europe’ includes Turkey (where Russian gas accounted for more than half of total gas consumption), the figure for the EU-28 is likely to be slightly lower. It is important to note that dependence on Russian gas imports is highly differentiated by region and between EU member states. The average level of gas import dependency (79.1%) and the average share of Russian gas in consumption (53.5%) for Central and South-Eastern Europe are both significantly higher than the EU averages (see table 1). Therefore, these states are more vulnerable to disruptions in Russian gas deliveries to Europe. When examining the importance of gas transit via Ukraine, it is misleading to frame the issue in terms of EU-28 energy security. Rather, it is an issue for a specific geographical part of the EU.
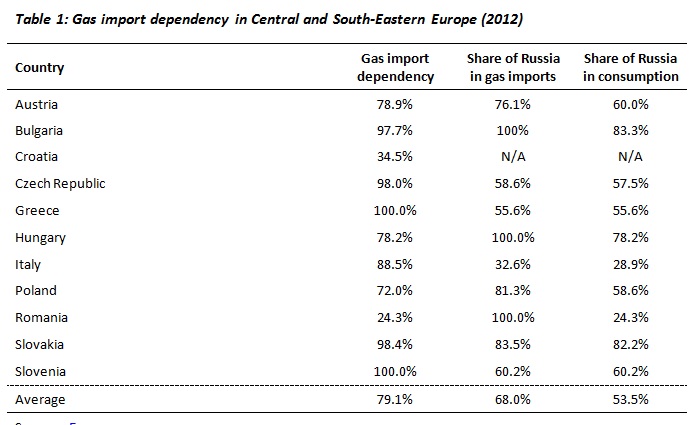
Sources: Eurogas
The role of Ukraine as a transit route for the delivery of Russian gas to Europe
Both the EU and Russia are dependent on fixed pipelines for the transit of gas. There are four main routes for Russian gas exports to the EU – direct pipelines to Finland and the Baltic States (collectively referred to hereafter as ‘Baltic exports’), the Nord Stream pipeline under the Baltic Sea to Germany, and transit pipelines via Belarus and Ukraine. There are some difficulties with calculating exact figures for the level of mutual dependence on these transit routes, however. The capacity of pipelines is significantly higher than the actual flows of gas supplies, which vary both annually and seasonally depending on demand (see table 2 and map 1). This time last year, for instance, 54.5% of Russia’s non-Baltic gas exports to the EU were transported via Ukraine to Hungary, Poland, Romania and Slovakia. By comparison, 17.4% was exported through the Nord Stream pipeline to Germany, while transit via Belarus to Poland accounted for 28.1%.
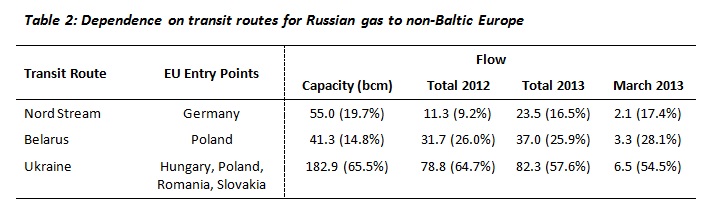
Volume figures in billion cubic metres. Percentages may not add up to 100 due to rounding errors.
Sources: IEA Gas Trade Flows in Europe; Nord Stream website
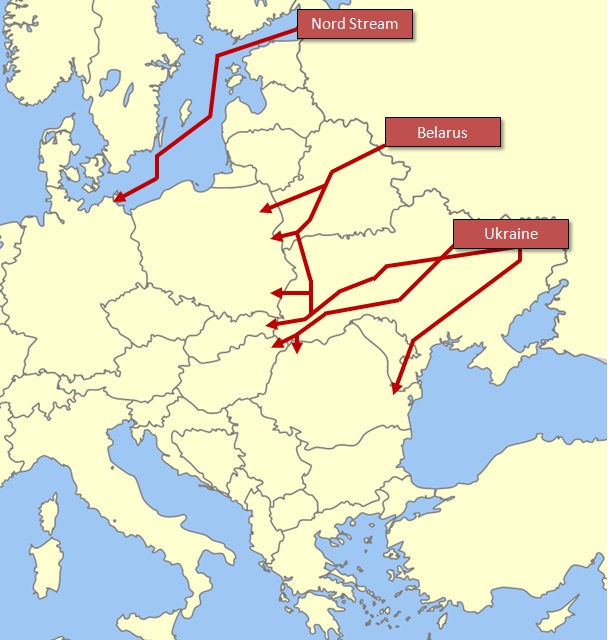
This multiplicity of transit routes has been developed with the explicit purpose of reducing Russia’s dependence on Ukraine as a transit state for deliveries of gas to Europe, which reached 90% in the early 1990s. The 33 bcm per year capacity Yamal-Europe pipeline (via Belarus) was constructed during the late 1990s, reaching full capacity in 2006. The 55 bcm per year capacity Nord Stream pipeline, direct from Russia to Germany under the Baltic Sea, was launched in two stages in 2011-12. However, the continued importance of Ukrainian gas transit for Italy, the Czech Republic, the Slovak Republic, Austria, Hungary, Slovenia, Croatia, Romania, Bulgaria, Greece, Serbia, Macedonia, and Bosnia-Herzegovina is illustrated by table 3.

Sources: IEA Gas Trade Flows in Europe
Lessons from the January 2009 gas supply disruption
The January 2009 gas dispute between Russia and Ukraine resulted in the most serious disruption of Russian gas supplies to Europe that the region had ever seen. The dispute, its origins, and its resolution have been examined in excellent detail by experts from the Oxford Institute of Energy Studies (Pirani, Stern, and Yafimava, 2009). For the purpose of this article, one of the most important details of the dispute was the highly differentiated impact the suspension of gas transit via Ukraine had on different European states, both EU members and non-EU members. This illustrated the disproportionate extent to which the states of Central and South-Eastern Europe were dependent on Russian gas supplies and Ukrainian gas transit in a ‘business as usual’ scenario. Furthermore, it demonstrated the limited ability of these states to source alternative supplies in an emergency situation (Kovacevic, 2009).
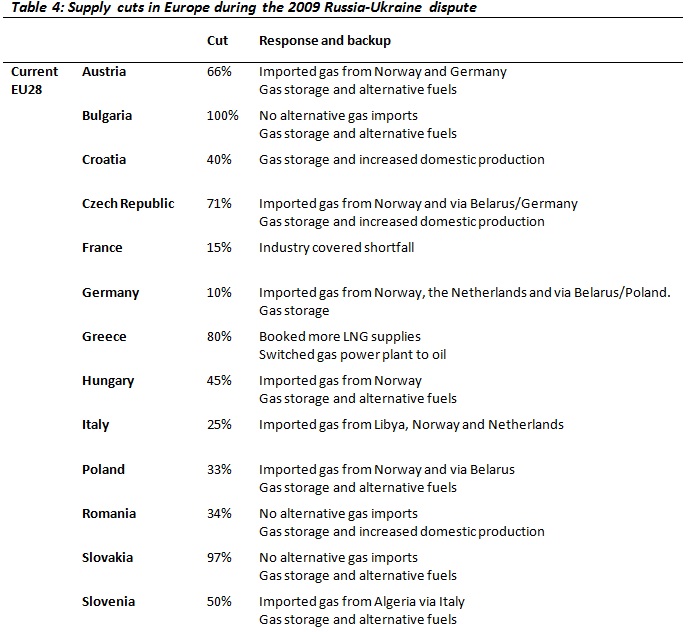

Source: Gas Coordination Group (2009) ‘Member State Situation According to Significance of Impact’, Memo 09/3, 9th January
Much has changed since 2009. As noted above, the first Nord Stream pipeline is now operational. Furthermore, the EU and its member states have made efforts to increase their readiness to respond to supply disruptions. This includes development of storage and reverse-flows on some interconnection pipelines between certain member states. Under EU regulation 994/2010, adopted by the EU following the 2009 disruption, member states are required to set out national preparatory action and emergency plans to prepare for and respond to supply disruptions should they occur. There remain, however, uncertainties about the EU’s ability to cope with a supply disruption through the Ukraine route on the scale of January 2009.
For instance, the Nord Stream pipeline now provides significantly more capacity for the transit of gas to non-Baltic Europe. If supplies were to be shut off on the Ukraine route, there is the possibility of rerouting supplies via Nord Stream and Belarus. To assess whether this is possible, we have analysed the daily flows for March of last year (which accounts for seasonal variation) through each of these routes, their total capacity, and their related spare capacity (see table 3).
Our analysis indicates that 208.7 mcm/day of Russian gas flowed via Ukraine, out of total Russian gas exports to (non-Baltic) Europe of 383.1 mcm/day. Therefore, transit via Ukraine accounted for 54.5% of Russia’s gas exports to (non-Baltic) Europe in March 2013. There existed 89.5 mcm/day of spare capacity on the non-Ukrainian routes, leaving 119.2 mcm/day (equivalent to 43.5 bcm per year) that would be non-deliverable in the case of a shutdown of Ukrainian transit. While figures for March 2014 will differ somewhat, this gives a clear indication that a supply shortfall due to disruption on the Ukraine route could not be entirely compensated for through alternative transit routes for Russian gas.
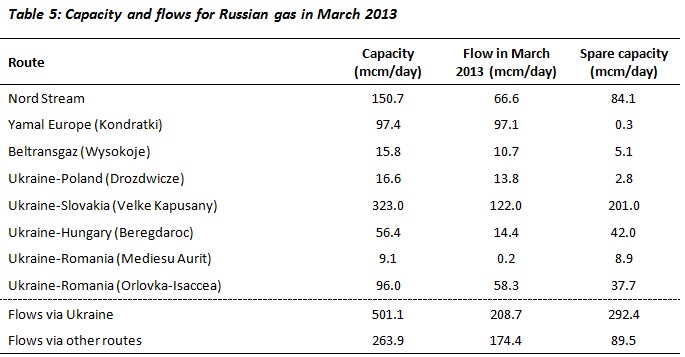
Sources: IEA Gas Trade Flows in Europe; Nord Stream website
There are other elements that would come into play in the event of a supply disruption such as alternative sources of gas supplies, particularly from Norway, Algeria, and LNG shipments. In recent days the Speaker of the U.S. House of Representatives, John Boehner, lent his support to a request from the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland and Slovakia to accelerate plans to export U.S. shale gas to Europe. While this may eventually contribute to greater diversification of EU supply, it will have no impact on any potential supply disruption over the coming months.
Gas storage will also be a key issue in the event of a short-term supply disruption. The tables below illustrate the current gas storage capacities and stocks of the states of Central and South-Eastern Europe in relation to their imports of Russian gas via Ukraine.
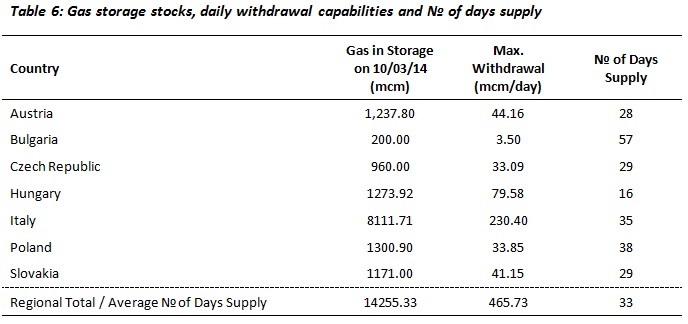
Sources: Gas Infrastructure Europe
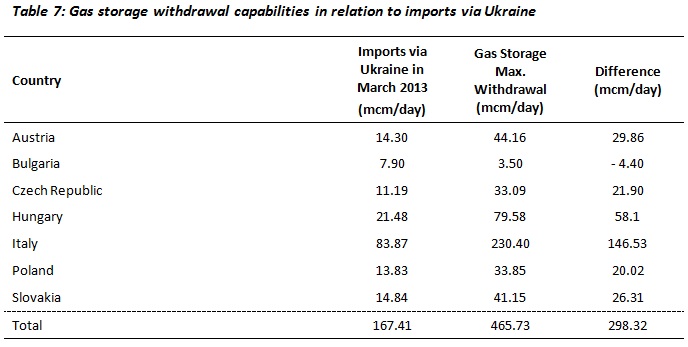
Sources: IEA Gas Trade Flows in Europe; Nord Stream website
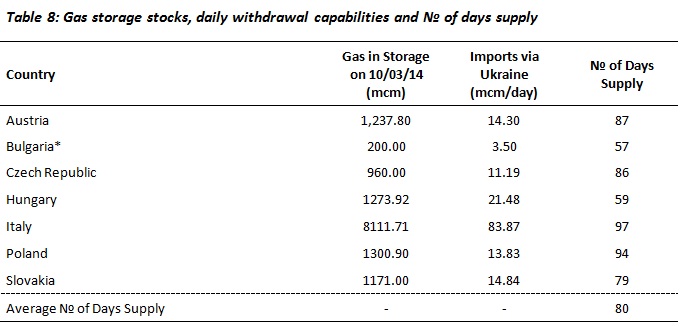
Sources: Gas Infrastructure Europe
* The figure of 3.50 mcm/d for Bulgaria is based on the maximum amount that can be withdrawn from Bulgarian gas storage facilities. This means that Bulgaria would suffer shortfalls, but could keep withdrawing gas from storage for 57 days if it withdrew the maximum possible amount every day.
As can be seen from the table above, Bulgaria is the only country whose gas storage facilities would not be sufficient to replace imports via Ukraine. Romania has no gas storage facilities, and so would be unable to provide extra supplies to Bulgaria. Romania has a 9.2 mcm/d cross-border connection with Western Ukraine (Mediesu Aurit) and could potentially gain access to Ukrainian gas storage, although this cannot be taken for granted. The Bulgarian cross-border connection with Greece cannot be reversed to take advantage of increased Greek LNG imports. Turkey would only be able to make up part of its shortfall by using spare capacity in the Blue Stream pipeline, and so would be unable to transit extra Russian gas supplies to Greece or to reverse the cross-border pipeline connection with Bulgaria. Macedonia relies completely on transit via Bulgaria for access to its Russian gas supplies. If Bulgaria faces a complete lack of imports, so too will Macedonia. Therefore, Bulgaria, Romania, and Macedonia would face significant shortfalls in their gas imports.
Although Greece has no gas storage facilities, in March 2013 Greek had 11.4 mcm/d of spare LNG import capacity, compared to 6.56 mcm/d of gas imports via Ukraine. Serbia receives its Russian gas imports via Hungary. In March 2013, these amounted to 4.15 mcm/d. Serbia has its own gas storage facility (Banatski Dvor), which has a capacity of 450 mcm and a maximum daily output of 5 mcm. It is not known how much gas Serbia has in storage, but gas withdrawals from Hungarian storage would be available for export to Serbia if Serbian gas stocks proved insufficient.
On this basis, Bulgaria, Romania, and Macedonia would face a serious deficit of gas supplies in the event of a suspension of gas transit via Ukraine. The other states in the region would be able to manage the situation as long as it did not last for more than approximately two months. Austria, Czech Republic, Hungary, Italy, Poland, and Slovakia currently have sufficient gas storage to withstand 2-3 months of disruption to their gas imports via Ukraine, while Serbia could draw on Hungarian gas stocks. Slovenia and Croatia could draw upon Italian, Austrian, and Hungarian gas stocks.
Gas flow from Russia to Europe via Ukraine in March 2013 was 208 mcm/d. Of this flow, 167.41 mcm/d was delivered to Austria, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Italy, Poland, and Slovakia. A further 4.95 mcm/d was delivered to Romania, 4.15 mcm/d to Serbia, 3.16 mcm/d to Slovenia, 3.96 mcm/d to Croatia, and 0.38 mcm/d to Macedonia. The total flow to Central and South-Eastern Europe was 184 mcm/d, meaning that just 24 mcm/d was delivered via Ukraine to Western Europe in March 2013. If similar flows were recorded in March 2014, the spare capacity of Nord Stream (84 mcm/d) would be more than sufficient to meet the additional needs of those Western European states that import Russian gas via Ukraine.
Conclusions
Russia-Ukraine gas relations are currently contextualised by tense political relations, and characterised by indebtedness and politically negotiated gas prices. With Naftogaz struggling to pay its debts to Gazprom and the discount on Russian gas supplies due to expire on the 1st of April, the current situation is every bit as serious as that which preceded the January 2009 dispute. In this regard, we are in agreement with experts from the Oxford Institute of Energy Studies (Pirani, Henderson, Honoure, Rogers, and Yafimava) that the combination of Naftogaz’s financial difficulties and the current political tensions “is the most likely potential cause of supply interruptions”. The one redeeming feature is that Gazprom and Naftogaz have existing gas supply and transit contracts that are not on the verge of expiry. Whilst we are not predicting a repeat of the January 2009 suspension of gas supplies to Ukraine, the possibility remains. Such a suspension would almost certainly result in the suspension of gas transit via Ukraine, as Naftogaz draws on its gas storage in the west of the country and reverses the flow of its pipelines to carry that gas back across Ukraine to consumers in the east of the country.
In the event of a suspension of gas transit via Ukraine, we find that the states of Central, Southern, and South-Eastern Europe would be disproportionately affected. The disruption of gas supplies to Western Europe would be small, and the spare capacity of Nord Stream could easily be used to make up the shortfall. Indeed, Nord Stream’s spare capacity could also be used to redirect flows to Central Europe, although much depends on the domestic pipeline capacities of those states and the ability to reverse those flows. Greece and Italy have the option of utilising their spare LNG import capacity. For the majority of those states that do not have access to alternative supplies, the issue of gas storage is crucial. Having examined current storage capacities and gas stocks, we find that the majority of states in the region are currently holding sufficient supplies to cope with a disruption of up to two months. Only Bulgaria, Romania, and Macedonia would be unable to gain access to sufficient supplies from gas storage. While the suspension of gas transit via Ukraine would be a significant event, it is not inevitable at this stage. If such a suspension does occur, most EU member states are well prepared and will be able to cope. The vulnerability of Bulgaria, Romania, and Macedonia should mark them out as a short-term priority for EU assistance in the event of a disruption. In the longer term, there clearly needs to be further development of cross-border interconnections and gas storage facilities in this region.
Bibliographic Information
 Jack Sharples is a lecturer in Energy Politics at the European University of St. Petersburg. He recently defended his PhD on Russian Gas Exports at the University of Glasgow and also writes the monthly ‘Gazprom Monitor’ report for the European Geopolitical Forum.
Jack Sharples is a lecturer in Energy Politics at the European University of St. Petersburg. He recently defended his PhD on Russian Gas Exports at the University of Glasgow and also writes the monthly ‘Gazprom Monitor’ report for the European Geopolitical Forum.
 Andy Judge is a researcher at the School of Government and Public Policy at the University of Strathclyde, Glasgow. He recently defended his PhD on Securitisation and European Natural Gas Policy and is currently working on research into the EU’s crisis response mechanisms in the event of gas supply disruptions. PDF Format
Andy Judge is a researcher at the School of Government and Public Policy at the University of Strathclyde, Glasgow. He recently defended his PhD on Securitisation and European Natural Gas Policy and is currently working on research into the EU’s crisis response mechanisms in the event of gas supply disruptions. PDF Format
 0 Pros
0 Pros 0 Cons
0 Cons
Comments 0